Sylhet Division on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Sylhet Division ( bn, সিলেট বিভাগ) is the northeastern
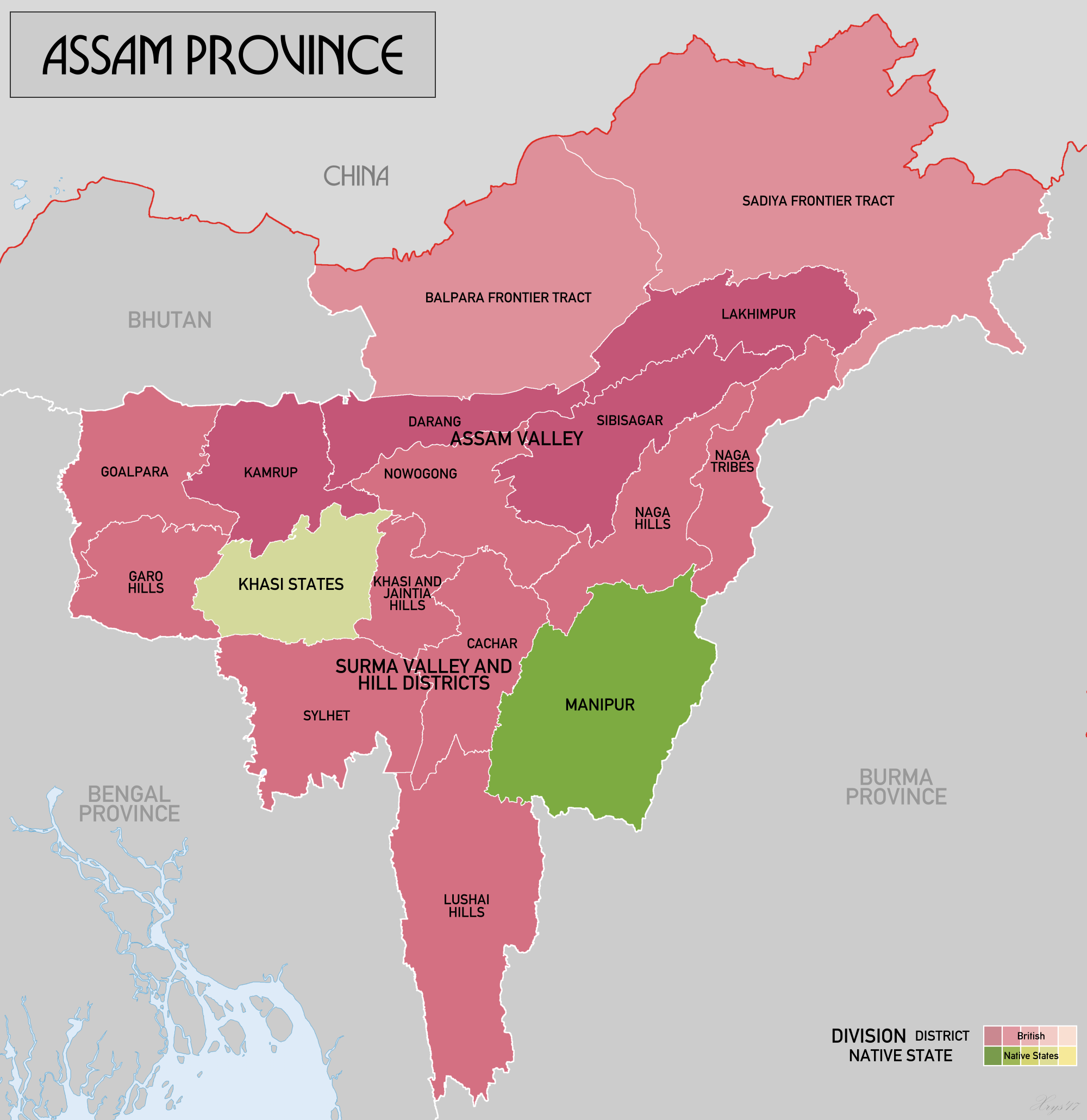 In 1874, the current Sylhet Division, which included
In 1874, the current Sylhet Division, which included
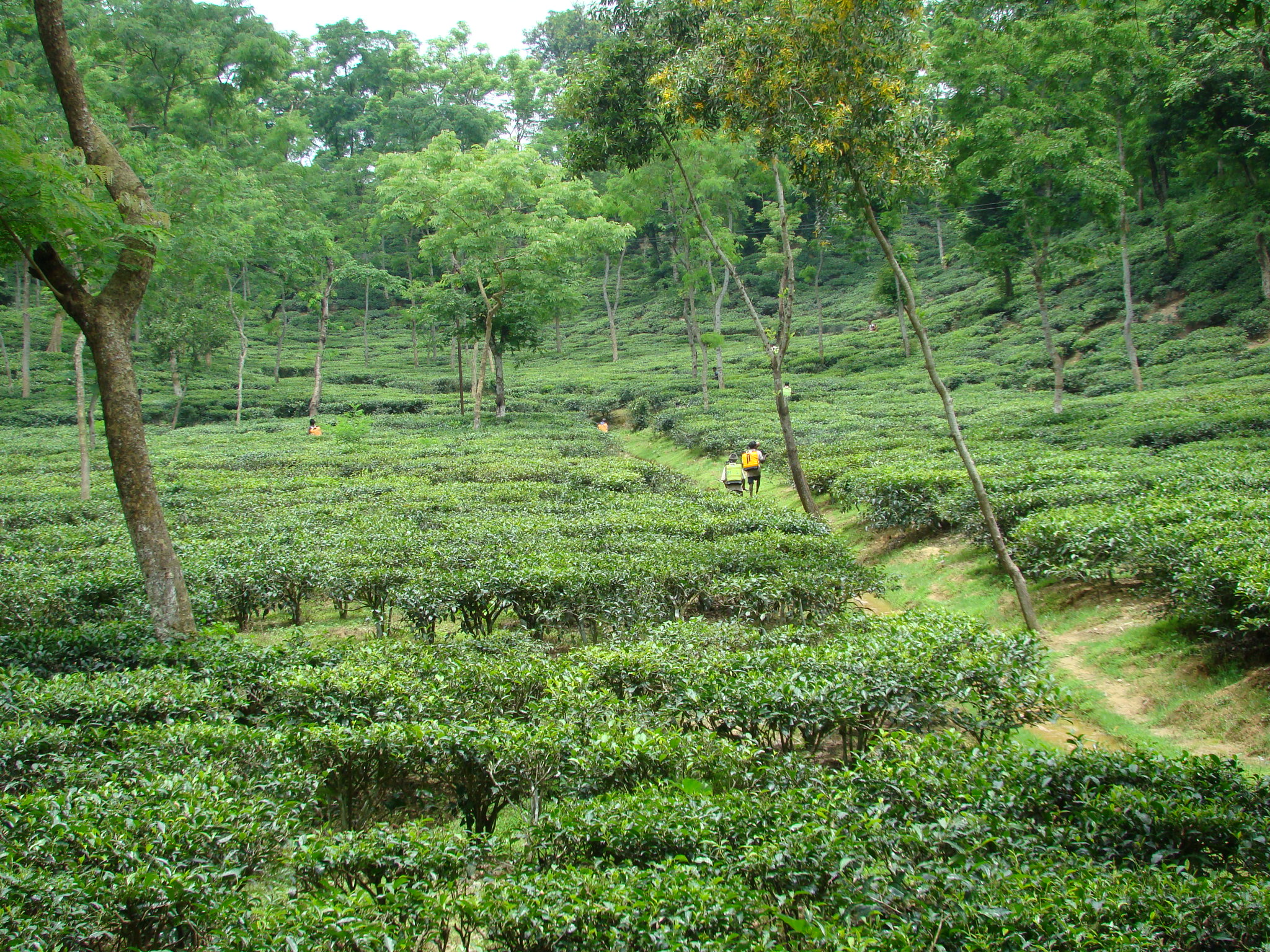 The area around Sylhet is a traditional tea growing area. The Surma Valley is covered with terraces of tea gardens and tropical forests.
The area around Sylhet is a traditional tea growing area. The Surma Valley is covered with terraces of tea gardens and tropical forests.

 In 1995, Sylhet split from the Chittagong Division and was declared the 6th division of the country. The Sylhet Division is overseen by the Divisional Commissioner, the current Divisional Commissioner is Md. Mashiur Rahman. The Sylhet Division is divided into four districts (
In 1995, Sylhet split from the Chittagong Division and was declared the 6th division of the country. The Sylhet Division is overseen by the Divisional Commissioner, the current Divisional Commissioner is Md. Mashiur Rahman. The Sylhet Division is divided into four districts (

 Geographically the region is surrounded by hillocks (known as ''tilla''s) from all three sides except its western plain boundary with the rest of
Geographically the region is surrounded by hillocks (known as ''tilla''s) from all three sides except its western plain boundary with the rest of
 The official language of Sylhet is
The official language of Sylhet is
Keane Bridge and Ali Amjad's Clock, Sylhet.jpg, Ali Amjad's Clock and
division
Division or divider may refer to:
Mathematics
*Division (mathematics), the inverse of multiplication
*Division algorithm, a method for computing the result of mathematical division
Military
*Division (military), a formation typically consisting ...
of Bangladesh
Bangladesh (}, ), officially the People's Republic of Bangladesh, is a country in South Asia. It is the eighth-most populous country in the world, with a population exceeding 165 million people in an area of . Bangladesh is among the mos ...
. It is bordered by the Indian states
India is a federal union comprising 28 states and 8 union territories, with a total of 36 entities. The states and union territories are further subdivided into districts and smaller administrative divisions.
History
Pre-indepen ...
of Meghalaya
Meghalaya (, or , meaning "abode of clouds"; from Sanskrit , "cloud" + , "abode") is a state in northeastern India. Meghalaya was formed on 21 January 1972 by carving out two districts from the state of Assam: (a) the United Khasi Hills and J ...
, Assam
Assam (; ) is a state in northeastern India, south of the eastern Himalayas along the Brahmaputra and Barak River valleys. Assam covers an area of . The state is bordered by Bhutan and Arunachal Pradesh to the north; Nagaland and Manipur ...
and Tripura
Tripura (, Bengali: ) is a state in Northeast India. The third-smallest state in the country, it covers ; and the seventh-least populous state with a population of 36.71 lakh ( 3.67 million). It is bordered by Assam and Mizoram to the ea ...
to the north, east and south respectively, and by the Bangladeshi divisions of Chittagong to the southwest and Dhaka
Dhaka ( or ; bn, ঢাকা, Ḍhākā, ), formerly known as Dacca, is the capital and largest city of Bangladesh, as well as the world's largest Bengali-speaking city. It is the eighth largest and sixth most densely populated city i ...
and Mymensingh
Mymensingh ( bn, ময়মনসিংহ) is the capital of Mymensingh Division, Bangladesh. Located on the bank of Brahmaputra River, about north of the national capital Dhaka, it is a major financial center and educational hub of north- ...
to the west. Prior to 1947, it included the subdivision of Karimganj
Karimganj is a city in the Karimganj District of the Indian state of Assam. It is the administrative headquarters of the district.
Karimganj city is located at . The area of Karimganj city is 16.09 km2. It has an average elevation of 13 ...
(presently in Barak Valley
The Barak Valley is located in the southern region of the Indian state of Assam. The region is named after the Barak river. The Barak valley consists of three administrative districts of Assam - namely Cachar, Karimganj, and Hailakandi. The ...
, India
India, officially the Republic of India (Hindi: ), is a country in South Asia. It is the seventh-largest country by area, the second-most populous country, and the most populous democracy in the world. Bounded by the Indian Ocean on the so ...
). However, Karimganj (including the thana
Thana means "police station" in South Asian countries, and can also mean the district controlled by a police station.
* Thanas of Bangladesh, former subdistricts in the administrative geography of Bangladesh; later renamed ''upazila''
* in (Briti ...
s of Badarpur, Patharkandi and Ratabari) was inexplicably severed from Sylhet by the Radcliffe Boundary Commission. According to Niharranjan Ray, it was partly due to a plea from a delegation led by Abdul Matlib Mazumdar
Abdul Matlib Mazumder ( bn, আব্দুল মতলিব মজুমদার; 1890–1980) was an Indian freedom fighter and political leader based in undivided Assam State. In 1946, when India was still under British rule, he became a ...
.
Etymology and names
The name ''Sylhet'' is an anglicisation of ''Shilhot'' (শিলহট). Its origins seem to come from theSanskrit
Sanskrit (; attributively , ; nominally , , ) is a classical language belonging to the Indo-Aryan branch of the Indo-European languages. It arose in South Asia after its predecessor languages had diffused there from the northwest in the late ...
words শিলা ''śilā'' (meaning 'stone') and হট্ট ''haṭṭa'' (meaning 'marketplace'). These words match the landscape and topography of the hilly region. The shila stones were abundant across Sylhet and King Gour Govinda
Govinda Fenchu ( bn, গোবিন্দ ফেঞ্চু), better known by his regnal title Gour Gobind ( bn, গৌড় গোবিন্দ) and also known by the sobriquet Shomudro Tonoy ( bn, সমুদ্র তনয়), was the ...
is known to have used stones to guard his capital. The word changed to Shilhot due to the elision of letter-final ''ô'' in the Bengali language
Bengali ( ), generally known by its endonym Bangla (, ), is an Indo-Aryan language native to the Bengal region of South Asia. It is the official, national, and most widely spoken language of Bangladesh and the second most widely spoken o ...
. Another theory is that it was named after Princess Sheela, the eldest daughter of Raja Guhak of the Jaintia Kingdom
The Jaintia Kingdom was a matrilineal kingdom in present-day Bangladesh's Sylhet Division and India's Meghalaya state. It was partitioned into three in 630 AD by Raja Guhak for his three sons, into the Jaintia Kingdom, Gour Kingdom and Laur ...
. It is said that Sheela was once bathing in a pond and was kidnapped. After being rescued by her father Raja Guhak, Sheela started to become more religious and live a secluded life. Sheela's died at a young age, the port-area which developed around the lake, which was the largest centre in northeastern Bengal for trade, was named Sheela haat
Haat or hat, even haat bazaar, is an open-air market that serves as a Trading post, trading venue for local people in rural areas and towns of Indian subcontinent, especially in India, Nepal, Bangladesh and Bhutan. Haat bazaars are conducted o ...
(or Sheela's marketplace) in her honour. Xuanzang
Xuanzang (, ; 602–664), born Chen Hui / Chen Yi (), also known as Hiuen Tsang, was a 7th-century Chinese Buddhist monk, scholar, traveler, and translator. He is known for the epoch-making contributions to Chinese Buddhism, the travelogue of ...
of China
China, officially the People's Republic of China (PRC), is a country in East Asia. It is the world's most populous country, with a population exceeding 1.4 billion, slightly ahead of India. China spans the equivalent of five time zones and ...
mentions that he visited a place called Sheelachatal in the 630s in his book, the ''Great Tang Records on the Western Regions
The ''Great Tang Records on the Western Regions'' is a narrative of Xuanzang's nineteen-year journey from Chang'an in central China to the Western Regions of Chinese historiography. The Buddhist scholar traveled through the Silk Road regions of ...
''. The Hattanath Tales mention Sheelachatal was named after both daughters of Guhak; Sheela and Chatala. Chatala indulged herself in an unlawful relationship with one of the palace servants, leading to her being disowned and dumped in a distant island in the middle of 2000 square mile lake to the south of the kingdom.
Mughal documents such as the Ain-i-Akbari referred to the region in Persian
Persian may refer to:
* People and things from Iran, historically called ''Persia'' in the English language
** Persians, the majority ethnic group in Iran, not to be conflated with the Iranic peoples
** Persian language, an Iranian language of the ...
as Silhet/Silhat (). Archaic European spellings included Sirote and Silhat. After the British arrived in the region in the 18th century, the spelling was changed from Silhat (সিলহট/ছিলট sil t) to Sylhet (সিলহেট/সিলেট sil t) so that it is distinct from the name of the nearby town of Silchar
Silchar is a city and the headquarters of the Cachar district of the state of Assam, India. It is located south east of Guwahati. It was founded by Captain Thomas Fisher in 1832 when he shifted the headquarters of Cachar to Janiganj in Silchar. ...
. The Anglicised spelling eventually also became the standard and official name in Modern Bengali.
An alternative name which may or may not have originated from ''Shilahatta'' was ''Srihotto'' (শ্রীহট্ট). The word ''sri
Shri (; , ) is a Sanskrit term denoting resplendence, wealth and prosperity, primarily used as an honorific.
The word is widely used in South and Southeast Asian languages such as Marathi, Malay (including Indonesian and Malaysian), Javanes ...
'' is a Sanskrit word for ''beauty''. This name was used in Kamarupa and the other petty kingdom
A petty kingdom is a kingdom described as minor or "petty" (from the French 'petit' meaning small) by contrast to an empire or unified kingdom that either preceded or succeeded it (e.g. the numerous kingdoms of Anglo-Saxon England unified into ...
s. In the Bengal Sultanate's inscriptions, Srihat/Sirhat () can be found as an administrative "Arsah". The earliest Sultanate inscription using this name was found in Shah Jalal's Dargah. Dating 1303, the inscription mentions Sikandar Khan Ghazi
Sikandar Khān Ghāzī ( fa, , bn, সিকান্দার খান গাজী) was the first wazir of Srihat under the Lakhnauti Kingdom ruled by Shamsuddin Firuz Shah. Prior to this, Khan was one of the commanders of the Battles of ...
's Conquest of Arsah Srihat with the help of Shah Jalal
Jalāl Mujarrad Kunyāʾī (), popularly known as Shah Jalal, was a celebrated Sufi figure of Bengal. His name is often associated with the Conquest of Sylhet and the spread of Islam into the region, part of a long history of interactions betw ...
, during the reign of Sultan Shamsuddin Firoz Shah.
After the Islamic Conquest of Sylhet
The Conquest of Sylhet ( bn, শ্রীহট্টের বিজয়, Srīhôtter Bijôy, Conquest of Srihatta) predominantly refers to an Islamic conquest of Srihatta (present-day Sylhet, Bangladesh) led by Sikandar Khan Ghazi, the mili ...
in 1303, the city colloquially became nicknamed as Jalalabad (জালালাবাদ). It is made up two words ''Jalal'' (), a name of Arabic
Arabic (, ' ; , ' or ) is a Semitic languages, Semitic language spoken primarily across the Arab world.Semitic languages: an international handbook / edited by Stefan Weninger; in collaboration with Geoffrey Khan, Michael P. Streck, Janet C ...
origin meaning majesty but in this case referring to Shah Jalal
Jalāl Mujarrad Kunyāʾī (), popularly known as Shah Jalal, was a celebrated Sufi figure of Bengal. His name is often associated with the Conquest of Sylhet and the spread of Islam into the region, part of a long history of interactions betw ...
, and '' Abad'' (), meaning settlement. This colloquial name continued to be used in the Mughal period
The Mughal Empire was an early-modern empire that controlled much of South Asia between the 16th and 19th centuries. Quote: "Although the first two Timurid emperors and many of their noblemen were recent migrants to the subcontinent, the d ...
. Currently, in the Sylhet City Corporation
Sylhet City Corporation (SCC) is a self-governing organisation which governs the municipal areas of Sylhet. This civic body of Sylhet
Sylhet ( bn, সিলেট) is a metropolitan city in northeastern Bangladesh. It is the administrative s ...
, there exists a metropolitan thana known as the Jalalabad Thana as well an area in its 7th ward.
History
 In 1874, the current Sylhet Division, which included
In 1874, the current Sylhet Division, which included Karimganj District
Karimganj district is one of the 34 districts of the Indian state of Assam. Karimganj town is both the administrative headquarters district and the biggest town of this district. It is located in southern Assam and borders Tripura and the Sylh ...
, was entirely known as the 'Sylhet district'. On 16 February 1874, Sylhet was separated from mainland Bengal to be made a part of the non-regulation Chief Commissioner's Province of Assam (Northeast Frontier Province) in order to facilitate Assam's commercial development. The people of Sylhet submitted a memorandum to the Viceroy protesting the inclusion in Assam. The protests subsided when the Viceroy, Lord Northbrook
Baron Northbrook, of Stratton in the County of Southampton, is a title in the Peerage of the United Kingdom. It was created in 1866 for the Liberal politician and former Chancellor of the Exchequer, Sir Francis Baring, 3rd Baronet. The holde ...
, visited Sylhet to reassure the people that education and justice would be administered from Bengal, and when the people in Sylhet saw the opportunity of employment in tea estates in Assam and a market for their produce. In 1905, Sylhet district rejoined Bengal as a part of the new ''Surma Valley Division'' of Eastern Bengal and Assam
Eastern Bengal and Assam was an administrative subdivision (province) of British India between 1905 and 1912. Headquartered in the city of Dacca, it covered territories in what are now Bangladesh, Northeast India and Northern West Bengal.
Hist ...
. In 1912, the then Sylhet district was once again moved to the newly created Assam Province
Assam Province was a province of British India, created in 1912 by the partition of the Eastern Bengal and Assam Province.
Its capital was in Shillong.
The Assam territory was first separated from Bengal in 1874 as the 'North-East Frontier' n ...
alongside the other districts of the Surma Valley Division.
Historically, the entire Sylhet region was a single district within the ''Surma Valley and Hill Districts'' Division as part of the Assam Province. In 1947, a referendum was held in the Sylhet district, the people of the whole district voting in favour of succession to Pakistan. However, the district's Karimganj subdivision was given to India by Cyril Radcliffe, after apparently being pleaded by a delegation led by Abdul Matlib Mazumdar
Abdul Matlib Mazumder ( bn, আব্দুল মতলিব মজুমদার; 1890–1980) was an Indian freedom fighter and political leader based in undivided Assam State. In 1946, when India was still under British rule, he became a ...
. The four other subdivisions ( North Sylhet, South Sylhet
Moulvibazar ( bn, মৌলভীবাজার) also spelled Maulvibazar, Moulavibazar, and Maulavibazar, (former South Sylhet) is the southeastern district of Sylhet Division in northeastern Bangladesh, named after the town of Moulvibazar. It i ...
, Habiganj
Habiganj ( bn, হবিগঞ্জ) is a major town and district headquarters of Habiganj District in the division of Sylhet, Bangladesh.
Population: Total population of Habiganj is about 95,000
Railroad
* Habiganj Bazar–Shaistaganj–B ...
and Sunamganj
Sunamganj ( bn, সুনামগঞ্জ) is a town in the Sylhet Division of northeastern Bangladesh. It is the administrative headquarters and largest town of Sunamganj District. It is located on the banks of the Surma River, approximately ...
) joined the Dominion of Pakistan
Between 14 August 1947 and 23 March 1956, Pakistan was an independent federal dominion in the Commonwealth of Nations, created by the passing of the Indian Independence Act 1947 by the British parliament, which also created the Dominion of ...
; subsequently forming East Bengal
ur,
, common_name = East Bengal
, status = Province of the Dominion of Pakistan
, p1 = Bengal Presidency
, flag_p1 = Flag of British Bengal.svg
, s1 = East ...
's 'Sylhet district' in the Chittagong division.
Following the Independence of Bangladesh in 1971, Sylhet became part of the newly formed country. In 1984, the four subdivisions of Sylhet district were upgraded to districts as part of H M Ershad
Lt. Gen. Hussain Muhammad Ershad ( bn, হুসেইন মুহাম্মদ এরশাদ; 1 February 1930 – 14 July 2019) was a Bangladeshi Army Chief politician who served as the President of Bangladesh from 1983 to 1990, a time ma ...
's decentralisation programme. The four districts remained in the Chittagong Division until 1995 when they formed the new Sylhet Division.
The Sylhet Division has a "friendship link" with the city of St Albans, in the United Kingdom. The link was established in 1988 when the St Albans District Council
The City and District of St Albans () is a local authority district in Hertfordshire in the East of England region. The main urban settlements are St Albans and Harpenden. The council offices are in St Albans.
History
St Albans City and D ...
supported a housing project in Sylhet as part of the International Year of Shelter for the Homeless. Sylhet was chosen because it is the area of origin for the largest ethnic minority group in St Albans. Sylhet also has many "friendship links" with other cities in the United Kingdom
The United Kingdom of Great Britain and Northern Ireland, commonly known as the United Kingdom (UK) or Britain, is a country in Europe, off the north-western coast of the continental mainland. It comprises England, Scotland, Wales and North ...
, as the majority of the half-million British Bangladeshis
British Bangladeshis ( bn, বিলাতী বাংলাদেশী, Bilatī Bangladeshī) are people of Bangladeshi origin who have attained citizenship in the United Kingdom, through immigration and historical naturalisation. The term c ...
have origins in Sylhet. This includes places such as Rochdale
Rochdale ( ) is a large town in Greater Manchester, England, at the foothills of the South Pennines in the dale on the River Roch, northwest of Oldham and northeast of Manchester. It is the administrative centre of the Metropolitan Borough ...
, Oldham
Oldham is a large town in Greater Manchester, England, amid the Pennines and between the rivers Irk and Medlock, southeast of Rochdale and northeast of Manchester. It is the administrative centre of the Metropolitan Borough of Oldham, wh ...
, London
London is the capital and largest city of England and the United Kingdom, with a population of just under 9 million. It stands on the River Thames in south-east England at the head of a estuary down to the North Sea, and has been a majo ...
, and many more places.
Economy
Srimangal
Sreemangal ( bn, শ্রীমঙ্গল, Srimongol) is an upazila of Moulvibazar District in the Sylhet Division of Bangladesh. It is located at the southwest of the district, and borders the Habiganj District to the west and the Indian state ...
is known as the tea capital of Bangladesh; for miles around, tea gardens are visible on the hill slopes.
The area has over 150 tea gardens, including three of the largest tea plantations in the world, both in terms of area and production. Nearly 300,000 workers, of which more than 75% are women, are employed on the tea estates. Employers prefer to engage women for plucking tea leaves since they do a better job than, but are paid less than, men. A recent drought has killed nearly a tenth of the tea shrubs.
The plantations, or gardens, were mostly developed during the British Raj
The British Raj (; from Hindi ''rāj'': kingdom, realm, state, or empire) was the rule of the British Crown on the Indian subcontinent;
*
* it is also called Crown rule in India,
*
*
*
*
or Direct rule in India,
* Quote: "Mill, who was himsel ...
. The plantations were started by the British, and the managers still live in the white timber houses built during the Raj. The bungalows stand on huge lawns. The service and the lifestyle of managers are still unchanged.
Numerous projects and businesses in the city
A city is a human settlement of notable size.Goodall, B. (1987) ''The Penguin Dictionary of Human Geography''. London: Penguin.Kuper, A. and Kuper, J., eds (1996) ''The Social Science Encyclopedia''. 2nd edition. London: Routledge. It can be def ...
and in large towns have been funded by Sylhetis living and working abroad. As of 1986, an estimated 95 percent of ethnic British Bangladeshi
British Bangladeshis ( bn, বিলাতী বাংলাদেশী, Bilatī Bangladeshī) are people of Bangladeshi origin who have attained citizenship in the United Kingdom, through immigration and historical naturalisation. The term c ...
s originated from or had ancestors from the Sylhet region. The Bangladesh government has set up a special Export Processing Zone
A free-trade zone (FTZ) is a class of special economic zone. It is a geographic area where goods may be imported, stored, handled, manufactured, or reconfigured and re- exported under specific customs regulation and generally not subject to cu ...
(EPZ) in Sylhet, in order to attract foreign investors, mainly from the UK.
Sylhet has also benefited from tourism. There are many natural landmarks people tend to visit, such as the Keane Bridge
The Keane Bridge is a notable landmark of Sylhet city, Bangladesh. This bridge is called ''the gateway to Sylhet city''.
After Earl Robert Miller, the ambassador of USA to Bangladesh visited the bridge and recommended its sole use as a pede ...
, Ali Amjad's Clock, Lalakhal, Jaflong
Jaflong ( bn, জাফলং) is a hill station and tourist destination in the Division of Sylhet, Bangladesh. It is located in Gowainghat Upazila of Sylhet District and situated at the border between Bangladesh and the Indian state of Meghal ...
, Madhabkunda waterfall
Madhabkunda waterfall ( bn, মাধবকুন্ড) is one of the highest waterfalls in Bangladesh. It is situated in Barlekha Upazila in Moulvibazar District. The waterfall is a popular tourist spot in Bangladesh. Big boulders, surrounding fo ...
, Ratargul Swamp Forest, Hakaluki Haor, Lawachara National Park
Lawachara National Park ( bn, লাউয়াছড়া) is a major national park and nature reserve in Bangladesh. The park is located at Kamalganj Upazila, Moulvibazar District in the northeastern region of the country. It is located with ...
, Tanguar Haor
Tanguar Haor ( bn, টাঙ্গুয়ার হাওর; also called Tangua haor), located in the Dharmapasha and Tahirpur upazilas of Sunamganj District in Bangladesh, is a unique wetland ecosystem of national importance and has come ...
and Bichnakandi
Bichnakandi ( bn, বিছানাকান্দি, Bichhanakandi), also known as Bisnakandi, is a village in Rustompur Union, Gowainghat Upazila of Bangladesh's Sylhet District. In recent years, there has been an influx of tourists to its ri ...
. Sylhet is also considered to be the spiritual capital of Bangladesh, due to the resting place of Shah Jalal
Jalāl Mujarrad Kunyāʾī (), popularly known as Shah Jalal, was a celebrated Sufi figure of Bengal. His name is often associated with the Conquest of Sylhet and the spread of Islam into the region, part of a long history of interactions betw ...
, a Sufi saint who spread Islam in Bangladesh, along with hundreds of his disciples. The Sylhet Shahi Eidgah is a famous place where Eid prayers take place and it is one of the largest Eidgahs in Bangladesh, built by Farhad Khan
Farhād Khān ( fa, , bn, ফরহাদ খাঁ), also known as Nizam-e-Zamanah ( bn, নিজাম-ই-জমানা) or Nizam-e-Zaman ( fa, ), was a Mughal military strategist who had many positions throughout his life. He was the m ...
during the reign of Mughal emperor Aurangzeb
Muhi al-Din Muhammad (; – 3 March 1707), commonly known as ( fa, , lit=Ornament of the Throne) and by his regnal title Alamgir ( fa, , translit=ʿĀlamgīr, lit=Conqueror of the World), was the sixth emperor of the Mughal Empire, ruling ...
. There are a number of hotels and resorts, particularly in Sreemangal Upazila and Bahubal Upazila.
Governance

 In 1995, Sylhet split from the Chittagong Division and was declared the 6th division of the country. The Sylhet Division is overseen by the Divisional Commissioner, the current Divisional Commissioner is Md. Mashiur Rahman. The Sylhet Division is divided into four districts (
In 1995, Sylhet split from the Chittagong Division and was declared the 6th division of the country. The Sylhet Division is overseen by the Divisional Commissioner, the current Divisional Commissioner is Md. Mashiur Rahman. The Sylhet Division is divided into four districts (Habiganj
Habiganj ( bn, হবিগঞ্জ) is a major town and district headquarters of Habiganj District in the division of Sylhet, Bangladesh.
Population: Total population of Habiganj is about 95,000
Railroad
* Habiganj Bazar–Shaistaganj–B ...
, Moulvibazar
Moulvibazar ( bn, মৌলভীবাজার) is a town in north-eastern Bangladesh just south of Sylhet. It is the capital of Moulvibazar Sadar Upazila and Moulvibazar District, and is located on the banks of the Manu River. The town has ...
, Sunamganj
Sunamganj ( bn, সুনামগঞ্জ) is a town in the Sylhet Division of northeastern Bangladesh. It is the administrative headquarters and largest town of Sunamganj District. It is located on the banks of the Surma River, approximately ...
and Sylhet) and further divided into 35 upazila
An ''upazila'' ( bn, উপজেলা, upôzela, lit=sub-district pronounced: ), formerly called ''thana'', is an administrative region in Bangladesh, functioning as a sub-unit of a district. It can be seen as an analogous to a county or a ...
s (sub-districts). These upazilas are further divided into 323 Union parishad
Union council ( bn, ইউনিয়ন পরিষদ, translit=iūniyan pariṣad, translit-std=IAST), also known as union parishad, rural council, rural union and simply union, is the smallest rural administrative and local government unit ...
s. Each union is roughly divided into 9 wards before going to village-level. There are roughly 10,185 villages in the Division. The Division hosts 19 Municipal corporation
A municipal corporation is the legal term for a local governing body, including (but not necessarily limited to) cities, counties, towns, townships, charter townships, villages, and boroughs. The term can also be used to describe municipally ...
s known as pourashavas, and one city corporation in Sylhet city. It also has 19 Parliamentary constituencies
An electoral district, also known as an election district, legislative district, voting district, constituency, riding, ward, division, or (election) precinct is a subdivision of a larger state (a country, administrative region, or other poli ...
. The headquarters of the Sylhet Division is the city of Sylhet in Sylhet Sadar Upazila
Sylhet Sadar ( bn, সিলেট সদর) is an upazila of Sylhet District in the Division of Sylhet, Bangladesh.
Geography
Sylhet Sadar is located at . It has 86,074 households and a total area of 323.17 km2. The city of Sylhet is loca ...
, Sylhet District. Pre-partition Sylhet's Karimganj
Karimganj is a city in the Karimganj District of the Indian state of Assam. It is the administrative headquarters of the district.
Karimganj city is located at . The area of Karimganj city is 16.09 km2. It has an average elevation of 13 ...
has been governed by India
India, officially the Republic of India (Hindi: ), is a country in South Asia. It is the seventh-largest country by area, the second-most populous country, and the most populous democracy in the world. Bounded by the Indian Ocean on the so ...
since 1947.
Geography

 Geographically the region is surrounded by hillocks (known as ''tilla''s) from all three sides except its western plain boundary with the rest of
Geographically the region is surrounded by hillocks (known as ''tilla''s) from all three sides except its western plain boundary with the rest of Bengal
Bengal ( ; bn, বাংলা/বঙ্গ, translit=Bānglā/Bôngô, ) is a geopolitical, cultural and historical region in South Asia, specifically in the eastern part of the Indian subcontinent at the apex of the Bay of Bengal, predom ...
. In the south of the region (Habiganj
Habiganj ( bn, হবিগঞ্জ) is a major town and district headquarters of Habiganj District in the division of Sylhet, Bangladesh.
Population: Total population of Habiganj is about 95,000
Railroad
* Habiganj Bazar–Shaistaganj–B ...
, Moulvibazar
Moulvibazar ( bn, মৌলভীবাজার) is a town in north-eastern Bangladesh just south of Sylhet. It is the capital of Moulvibazar Sadar Upazila and Moulvibazar District, and is located on the banks of the Manu River. The town has ...
), eight hill ranges enter the plains of Sylhet running uniformly from the west to the east. They are: Raghunandan, Dinarpur-Shatgaon, Balishira, Bhanugach-Rajkandi, Hararganj-Singla, Patharia, Pratapgarh-Duhalia and Sorrispur-Siddheswar hill ranges. At the centre of the region is also an isolated range known as the Ita Hills.
The region is considered one of the most picturesque and archaeologically rich regions in South Asia
South Asia is the southern subregion of Asia, which is defined in both geographical and ethno-cultural terms. The region consists of the countries of Afghanistan, Bangladesh, Bhutan, India, Maldives, Nepal, Pakistan, and Sri Lanka.;;;;;;;; ...
. It is home to three national parks; the Lawachara National Park
Lawachara National Park ( bn, লাউয়াছড়া) is a major national park and nature reserve in Bangladesh. The park is located at Kamalganj Upazila, Moulvibazar District in the northeastern region of the country. It is located with ...
, Khadim Nagar National Park and Satchari National Park
Satchari National Park ( bn, সাতছড়ি) is a national park in Habiganj District, Bangladesh. After the 1974 Wild Life Preservation Act, in 2005 Satchari National Park was built on of land. Literally 'Satchari' in Bengali means 'Sev ...
, as well as numerous smaller parks and forests such as the Ratargul Swamp Forest, Rema-Kalenga Wildlife Sanctuary
Rema-Kalenga Wildlife Sanctuary is a protected forest and wildlife sanctuary in Bangladesh. This is a dry and evergreen forest . It is located in the Chunarughat of Habiganj district. Rema-Kalenga Wildlife Sanctuary was established in 1982 and l ...
. Its burgeoning economy has contributed to the regional attractions of landscapes filled with fragrant orange and pineapple gardens as well as tea plantations. The region has a tropical monsoon climate
An area of tropical monsoon climate (occasionally known as a sub-equatorial, tropical wet climate or a tropical monsoon and trade-wind littoral climate) is a tropical climate sub-type that corresponds to the Köppen climate classification category ...
(Köppen Köppen is a German surname. Notable people with the surname include:
* Bernd Köppen (born 1951), German pianist and composer
* Carl Köppen (1833-1907), German military advisor in Meiji era Japan
* Edlef Köppen (1893–1939), German author and ...
''Am'') bordering on a humid subtropical climate (''Cwa'') at higher elevations. The rainy season from April to October is hot and humid with very heavy showers and thunderstorms almost every day, whilst the short dry season from November to February is very warm and fairly clear. Nearly 80% of the annual average rainfall of occurs between May and September.
The physiography
Physical geography (also known as physiography) is one of the three main branches of geography. Physical geography is the branch of natural science which deals with the processes and patterns in the natural environment such as the atmosphere, h ...
of the division consists mainly of hill soils, encompassing a few large depressions known locally as " beels" which can be mainly classified as oxbow lakes, caused by tectonic subsidence primarily during the earthquake of 1762.
Geologically, the division is complex having diverse sacrificial geomorphology; high topography of Plio-Miocene
The Miocene ( ) is the first geological epoch of the Neogene Period and extends from about (Ma). The Miocene was named by Scottish geologist Charles Lyell; the name comes from the Greek words (', "less") and (', "new") and means "less recen ...
age such as the Khasi and Jaintia Hills
The Khasi and Jaintia Hills are a mountainous region that was mainly part of Assam and Meghalaya. This area is now part of the present Indian constitutive state of Meghalaya (formerly part of Assam), which includes the present districts of East ...
and small hillocks along the border. At the centre there is a vast low laying flood plain of recent origin with saucer shaped depressions, locally called ''haor
A ( bn, হাওর) is a wetland ecosystem in the north eastern part of Bangladesh which physically is a bowl or saucer shaped shallow depression, also known as a backswamp.MK Alam; ''Wave attack in Haor areas of Bangladesh and cement conc ...
s''. There are many haors in the region and the largest ones include Hakaluki, Kawadighi, Tanguar and Hail. Available limestone deposits in different parts of the region suggest that the whole area was under the ocean in the Oligo-Miocene
The Miocene ( ) is the first geological epoch of the Neogene Period and extends from about (Ma). The Miocene was named by Scottish geologist Charles Lyell; the name comes from the Greek words (', "less") and (', "new") and means "less recen ...
. In the last 150 years, three major earthquakes hit the city, at a magnitude of at least 7.5 on the Richter Scale
The Richter scale —also called the Richter magnitude scale, Richter's magnitude scale, and the Gutenberg–Richter scale—is a measure of the strength of earthquakes, developed by Charles Francis Richter and presented in his landmark 1935 ...
, the last one took place in 1918, although many people are unaware that Sylhet lies on an earthquake prone zone.
Flora and fauna
The region is home to theAsian elephant
The Asian elephant (''Elephas maximus''), also known as the Asiatic elephant, is the only living species of the genus ''Elephas'' and is distributed throughout the Indian subcontinent and Southeast Asia, from India in the west, Nepal in the no ...
and the One-horned rhinoceros
''Rhinoceros'' is a genus comprising one-horned rhinoceroses. This scientific name was proposed by Swedish taxonomist Carl Linnaeus in 1758. The genus contains two species, the Indian rhinoceros (''Rhinoceros unicornis'') and the Javan rhinocer ...
, mostly towards the south. Tigers and leopards were once found throughout the region. Other notable fauna include the Sambar deer, Indian hog deer
The Indian hog deer (''Axis porcinus'') is a small deer native to the Indo-Gangetic Plain in Pakistan, northern India, Nepal, Bangladesh to mainland Southeast Asia. It also occurs in western Thailand, and is possibly extirpated from China (in s ...
, Sylhet hara and Sylhet roofed turtle.
The Asian elephant were once found in small numbers in places such as Chapghat, Bhanugach, Chamtolla, Mahram and the Raghunandan hills. More abundantly they are found near streams in Singla and Langai.
Culture
Language
 The official language of Sylhet is
The official language of Sylhet is Bengali
Bengali or Bengalee, or Bengalese may refer to:
*something of, from, or related to Bengal, a large region in South Asia
* Bengalis, an ethnic and linguistic group of the region
* Bengali language, the language they speak
** Bengali alphabet, the w ...
. It is used in education and all government affairs in the division. The Adivasi
The Adivasi refers to inhabitants of Indian subcontinent, generally tribal people. The term is a Sanskrit word coined in the 1930s by political activists to give the tribal people an indigenous identity by claiming an indigenous origin. The term ...
(indigenous) and tea labourers brought over during the British colonial rule also have their own native languages such as Khasi, Kuki, Laiunghtor, Meitei, Bishnupriya Manipuri
Bishnupriya Manipuri, also known as simply Bishnupriya, is an Indo-Aryan language belonging to the Bengali–Assamese languages, Bengali–Assamese linguistic sub-branch. It is a creole language, creole of Bengali language and Meitei languag ...
, Hajong, Garo
Garo may refer to:
People and languages
* Garo people, a tribal people in India
** Garo language, the language spoken by the Garo tribe
Places
* Kingdom of Garo, a former kingdom in southern Ethiopia
* Garo, Colorado
* Garo Hills, part of the Ga ...
, Odia, Kurmi creole, Hindi
Hindi (Devanāgarī: or , ), or more precisely Modern Standard Hindi (Devanagari: ), is an Indo-Aryan language spoken chiefly in the Hindi Belt region encompassing parts of northern, central, eastern, and western India. Hindi has been de ...
, Bhumij and Tripuri
Tripuri refer to:
*Tripuri people, an ethnic group in India and Bangladesh, also known as Tipra people
**Tripuri language
**Tripuri nationalism
**Tripuri calendar
**Tripuri culture
**Tripuri cuisine
**Tripuri dances
**Tripuri dress
**Tripuri games ...
.
Architecture
The intense building of mosques which took place during the Sultanate era indicates the rapidity with which the locals converted to Islam. Today, mosques are present in every Muslim-inhabited village. Bengali mosques are normally covered with several small domes and curved brick roofs decorated withterracotta
Terracotta, terra cotta, or terra-cotta (; ; ), in its material sense as an earthenware substrate, is a clay-based unglazed or glazed ceramic where the fired body is porous.
In applied art, craft, construction, and architecture, terracotta ...
. Ponds
A pond is an area filled with water, either natural or artificial, that is smaller than a lake. Defining them to be less than in area, less than deep, and with less than 30% emergent vegetation helps in distinguishing their ecology from t ...
are often located beside a mosque.
Faujdar
Faujdar is a term of pre-Mughal origins. Under the Mughals it was an office that combined the functions of a military commander along with judicial and land revenue functions.
In pre-Mughal times, the term referred to a military officer but d ...
Farhad Khan
Farhād Khān ( fa, , bn, ফরহাদ খাঁ), also known as Nizam-e-Zamanah ( bn, নিজাম-ই-জমানা) or Nizam-e-Zaman ( fa, ), was a Mughal military strategist who had many positions throughout his life. He was the m ...
built Sylhet Shahi Eidgah in the 1660s under the reign of Mughal Emperor
The Mughal emperors ( fa, , Pādishāhān) were the supreme heads of state of the Mughal Empire on the Indian subcontinent, mainly corresponding to the modern countries of India, Pakistan, Afghanistan and Bangladesh. The Mughal rulers styled t ...
Aurangzeb
Muhi al-Din Muhammad (; – 3 March 1707), commonly known as ( fa, , lit=Ornament of the Throne) and by his regnal title Alamgir ( fa, , translit=ʿĀlamgīr, lit=Conqueror of the World), was the sixth emperor of the Mughal Empire, ruling ...
. It stands as the largest eidgah
Eidgah or Idgah, also Eid Gah or Id Gah ( fa, "site of Eid bservances; bn, ঈদগাহ; pnb, ; ur, ; hi, ईदगाह) is a term used in South Asian Islamic culture for the open-air enclosure usually outside the city (or at th ...
of the region.
In 1872, Nawab Moulvi Ali Ahmed Khan of Prithimpassa
The Prithimpassa family, also known as the Nawabs of Longla, are an royal family from the Prithimpassa Union, Kulaura Upazila, Moulvibazar, Sylhet, Bangladesh. The family was of the erstwhile feudal nobility of East Bengal. They played importan ...
constructed Ali Amjad's Clock, named after his son, in Sylhet City. In 1936, a bridge was constructed across the Surma River
The Surma River ( bn, সুরমা নদী) is a major river in Bangladesh, part of the Surma-Meghna River System. It starts when the Barak River from northeast India divides at the Bangladesh border into the Surma and the Kushiyara rivers. ...
known as the Keane Bridge
The Keane Bridge is a notable landmark of Sylhet city, Bangladesh. This bridge is called ''the gateway to Sylhet city''.
After Earl Robert Miller, the ambassador of USA to Bangladesh visited the bridge and recommended its sole use as a pede ...
. These two historic landmarks are known as the ''gateway to Sylhet city''.
Assam-type architecture
Assam-type architecture is an architectural style developed in the state of Assam in India during the late modern period. It is found in Assam and Sylhet region. The houses constructed using this style are generally termed as ''Assam-type'' ho ...
developed in Sylhet region under Assam Province
Assam Province was a province of British India, created in 1912 by the partition of the Eastern Bengal and Assam Province.
Its capital was in Shillong.
The Assam territory was first separated from Bengal in 1874 as the 'North-East Frontier' n ...
during the late modern period.
Keane Bridge
The Keane Bridge is a notable landmark of Sylhet city, Bangladesh. This bridge is called ''the gateway to Sylhet city''.
After Earl Robert Miller, the ambassador of USA to Bangladesh visited the bridge and recommended its sole use as a pede ...
Uchail mosque 1.jpg, Shankarpasha Shahi Masjid
Shankarpasha Shahi Jame Masjid, ( bn, উচাইল শংকরপাশা শাহী মসজিদ, fa, شاهي مسجد شنكرپاشا) is an ancient mosque in the Habiganj Sadar Upazila of Bangladesh. It was built during the 15th ce ...
পাগলার বড় মসজিদ,সুনামগঞ্জ,সিলেট।.JPG, Pagla Jame Masjid
File:Night View of Sylhet Shahi Eidgah.jpg, Sylhet Shahi Eidgah entrance
File:Eatopia_Restaurant,_Sylhet.jpg, Modern architecture in Sylhet
Sports and games
Cricket
Cricket is a bat-and-ball game played between two teams of eleven players on a field at the centre of which is a pitch with a wicket at each end, each comprising two bails balanced on three stumps. The batting side scores runs by striki ...
is the most popular sport in Sylhet. Regional cricket teams include Sylhet Thunder, East Zone
The East Zone cricket team is a first-class cricket team that represents eastern India in the Duleep Trophy and Syed Mushtaq Ali Trophy Inter Zonal. It is a composite team of five first-class Indian teams from eastern India competing in the Ranj ...
and the Sylhet Division cricket team. Football is also a common sport and the multi-use Saifur Rahman Stadium are known to host football matches. Beanibazar SC
Beanibazar Sporting Club is a Bangladeshi association football, football club from Beanibazar, Sylhet.
History
Beanibazar Sporting Club was formed in 2009 as a professional football club to take part in the Bangladesh League, Bangladesh Premier ...
has played in the Bangladesh League
Bangladesh (}, ), officially the People's Republic of Bangladesh, is a country in South Asia. It is the eighth-most populous country in the world, with a population exceeding 165 million people in an area of . Bangladesh is among the mos ...
. The home stadium of the football club, Sheikh Russel KC
Sheikh Russel KC is a professional football club based in Dhaka, Bangladesh, currently playing in the Bangladesh Premier League. The club has won the Federation Cup in 2012, which was their first major title. They also won their maiden Banglade ...
, is in Sylhet District Stadium. Board and home games such as Dosh Fochish and its modern counterpart Ludo, as well as Carrom Board
Carrom is a tabletop game of Indian origin in which players flick discs, attempting to knock them to the corners of the board. The game is very popular in the Indian subcontinent, and is known by various names in different languages. In Sou ...
, Sur-Fulish, Khanamasi and Chess
Chess is a board game for two players, called White and Black, each controlling an army of chess pieces in their color, with the objective to checkmate the opponent's king. It is sometimes called international chess or Western chess to dist ...
, are very popular in the region. Nowka Bais is a common traditional rowing competition during the monsoon season when rivers are filled up, and much of the land is under water. Fighting sports include Kabaddi
Kabaddi is a contact team sport. Played between two teams of seven players, the objective of the game is for a single player on offence, referred to as a "raider", to run into the opposing team's half of the court, touch out as many of their ...
, Latim and Lathi khela
Lathi khela ( bn, লাঠি খেলা) is a traditional Bengali martial art – a kind of stick fighting practised India and Bangladesh. A practitioner is known as a ''lathial''.
Etymology
The word ''lathi'' is the Bengali word meaning s ...
.
Demography
The division's population is over 12 million andBengalis
Bengalis (singular Bengali bn, বাঙ্গালী/বাঙালি ), also rendered as Bangalee or the Bengali people, are an Indo-Aryan ethnolinguistic group originating from and culturally affiliated with the Bengal region of ...
make up a large majority of the region's population. The tribal and Adivasi
The Adivasi refers to inhabitants of Indian subcontinent, generally tribal people. The term is a Sanskrit word coined in the 1930s by political activists to give the tribal people an indigenous identity by claiming an indigenous origin. The term ...
population tend to live in secluded rural areas of the region primarily near the hills and tea gardens. They are made up of several ethnic groups such as the Bishnupriya Manipuri
Bishnupriya Manipuri, also known as simply Bishnupriya, is an Indo-Aryan language belonging to the Bengali–Assamese languages, Bengali–Assamese linguistic sub-branch. It is a creole language, creole of Bengali language and Meitei languag ...
s, Khasi, Laleng
The Laleng, also known as the Patra ( bn, পাত্র, Patro) are a small indigenous ethnolinguistic group primarily living deep in the forests of Sylhet District and Moulvibazar District in Bangladesh. They speak the endangered Laiunghtor ...
s, Tripuri
Tripuri refer to:
*Tripuri people, an ethnic group in India and Bangladesh, also known as Tipra people
**Tripuri language
**Tripuri nationalism
**Tripuri calendar
**Tripuri culture
**Tripuri cuisine
**Tripuri dances
**Tripuri dress
**Tripuri games ...
s, Meiteis, Garo
Garo may refer to:
People and languages
* Garo people, a tribal people in India
** Garo language, the language spoken by the Garo tribe
Places
* Kingdom of Garo, a former kingdom in southern Ethiopia
* Garo, Colorado
* Garo Hills, part of the Ga ...
s, and Kukis. In the nineteenth century, the British brought over indigenous peoples from other parts of British India
The provinces of India, earlier presidencies of British India and still earlier, presidency towns, were the administrative divisions of British governance on the Indian subcontinent. Collectively, they have been called British India. In one ...
to work as tea garden labourers such as the Kurmi
Kurmi is traditionally a non-elite tiller caste in the lower Gangetic plain of India, especially southern regions of Awadh, eastern Uttar Pradesh and parts of Bihar. The Kurmis came to be known for their exceptional work ethic, superior til ...
s, Musahars, Bauris The Bauris (Bengali:বাউরী) are recognised as an indigenous Bhil Subgroup of Bengali Hindu community, belonging to the Kashyapa clan and Shakta sect of hinduism, primarily residing in Bengal found in large numbers in Bankura, Birbhum, Puru ...
, Beens, Bonaz, Sabar
The sabar is a traditional drum from Senegal that is also played in the Gambia. It is associated with Wolof and Serer people.Bhumij amongst others.
Religion
Islam
Islam (; ar, ۘالِإسلَام, , ) is an Abrahamic religions, Abrahamic Monotheism#Islam, monotheistic religion centred primarily around the Quran, a religious text considered by Muslims to be the direct word of God in Islam, God (or ...
is the largest religion in the whole region practised by the Bengali Muslims
Bengali Muslims ( bn, বাঙালি মুসলমান; ) are adherents of Islam who ethnically, linguistically and genealogically identify as Bengalis. Comprising about two-thirds of the global Bengali population, they are the sec ...
. Sunni Islam is the largest denomination with majority following the Hanafi
The Hanafi school ( ar, حَنَفِية, translit=Ḥanafiyah; also called Hanafite in English), Hanafism, or the Hanafi fiqh, is the oldest and one of the four traditional major Sunni schools ( maddhab) of Islamic Law (Fiqh). It is named a ...
school of law although some also follow the Shafi'i
The Shafii ( ar, شَافِعِي, translit=Shāfiʿī, also spelled Shafei) school, also known as Madhhab al-Shāfiʿī, is one of the four major traditional schools of religious law (madhhab) in the Sunnī branch of Islam. It was founded by ...
and Hanbali
The Hanbali school ( ar, ٱلْمَذْهَب ٱلْحَنۢبَلِي, al-maḏhab al-ḥanbalī) is one of the four major traditional Sunni schools (''madhahib'') of Islamic jurisprudence. It is named after the Arab scholar Ahmad ibn Hanbal ...
madhhab
A ( ar, مذهب ', , "way to act". pl. مَذَاهِب , ) is a school of thought within ''fiqh'' (Islamic jurisprudence).
The major Sunni Mathhab are Hanafi, Maliki, Shafi'i and Hanbali.
They emerged in the ninth and tenth centuries CE a ...
s. There are significant numbers of people who follow Sufi ideals similar to the Barelvis, the most influential is the teachings of Abdul Latif Chowdhury Fultali
Abdul Latif Chowdhury ( bn, আব্দুল লতিফ চৌধুরী; 25 May 1913 – 16 January 2008), widely known as Saheb Qiblah Fultali, was a Bangladeshi Sufi Islamic scholar and theologian who is the founder of the Fultali movem ...
of Zakiganj – a descendant of one of the disciples of Shah Jalal
Jalāl Mujarrad Kunyāʾī (), popularly known as Shah Jalal, was a celebrated Sufi figure of Bengal. His name is often associated with the Conquest of Sylhet and the spread of Islam into the region, part of a long history of interactions betw ...
. The revivalist Deobandi movement is also popular in the region with Jamia Tawakkulia Renga being a notable centre and many are part of the Tablighi Jamaat
Tablighi Jamaat (, also translated as "propagation party" or "preaching party")
is a transnational Deobandi Islamic Dawah, missionary movement
that focuses on exhorting Muslims to be more religiously observant
and encouraging fellow memb ...
. Haji Shariatullah
Haji Shariatullah ( bn, হাজী শরীয়তুল্লাহ; 17811840) was a prominent religious leader and Islamic scholar from Bengal in the eastern subcontinent, who is best known as the founder of the Faraizi movement. In 1884, ...
's Faraizi movement
The Faraizi movement ( bn, ফরায়েজি আন্দোলন, fôrayeji andolon) was a movement led by Haji Shariatullah in Eastern Bengal to give up un-Islamic practices and act upon their duties as Muslims ( ''farāʾiḍ''). F ...
was very popular during the British period and Wahhabism
Wahhabism ( ar, ٱلْوَهَّابِيَةُ, translit=al-Wahhābiyyah) is a Sunni Islamic revivalist and fundamentalist movement associated with the reformist doctrines of the 18th-century Arabian Islamic scholar, theologian, preacher, and ...
is adopted by some upper-class families. The Ahmadiyya
Ahmadiyya (, ), officially the Ahmadiyya Muslim Community or the Ahmadiyya Muslim Jama'at (AMJ, ar, الجماعة الإسلامية الأحمدية, al-Jamāʿah al-Islāmīyah al-Aḥmadīyah; ur, , translit=Jamā'at Aḥmadiyyah Musl ...
community is mostly concentrated in Selbaras, which was the ancestral home of Ahmad Toufiq Choudhury, the leader of Ahmadiyya Muslim Jama'at Bangladesh.
There is a very small minority of Shia Muslims
Shīʿa Islam or Shīʿīsm is the second-largest branch of Islam. It holds that the Islamic prophet Muhammad designated ʿAlī ibn Abī Ṭālib as his successor (''khalīfa'') and the Imam (spiritual and political leader) after him, mos ...
who gather every year during Ashura for the Mourning of Muharram
The Mourning of Muharram (also known as Azadari, Remembrance of Muharram or Muharram Observances) is a set of commemoration rituals observed primarily by Shia people. The commemoration falls in Muharram, the first month of the Islamic calendar. ...
processions. Places of procession include the Prithimpasha Nawab Bari in Kulaura
Kulaura ( bn, কুলাউড়া) is the biggest upazila (subdistrict) of the Moulvibazar District in north-eastern Bangladesh. The total area of this upazila is 545 km2. Hakaluki Haor, the largest marsh wetland in Sylhet and one of the ...
, home to a Shia family, as well as Rajtila.
Hinduism
Hinduism () is an Indian religion or '' dharma'', a religious and universal order or way of life by which followers abide. As a religion, it is the world's third-largest, with over 1.2–1.35 billion followers, or 15–16% of the global p ...
is the second largest religion practised by the Bengali Hindus
Bengali Hindus ( bn, বাঙ্গালী হিন্দু/বাঙালি হিন্দু, translit=Bāṅgālī Hindu/Bāṅāli Hindu) are an ethnoreligious population who make up the majority in the Indian states of West Beng ...
as well as majority of the Bishnupriya Manipuri
Bishnupriya Manipuri, also known as simply Bishnupriya, is an Indo-Aryan language belonging to the Bengali–Assamese languages, Bengali–Assamese linguistic sub-branch. It is a creole language, creole of Bengali language and Meitei languag ...
, Beens, Bhumij, Bonaz, Sabar
The sabar is a traditional drum from Senegal that is also played in the Gambia. It is associated with Wolof and Serer people.Musahar,
Kurmi
Kurmi is traditionally a non-elite tiller caste in the lower Gangetic plain of India, especially southern regions of Awadh, eastern Uttar Pradesh and parts of Bihar. The Kurmis came to be known for their exceptional work ethic, superior til ...
, Laleng
The Laleng, also known as the Patra ( bn, পাত্র, Patro) are a small indigenous ethnolinguistic group primarily living deep in the forests of Sylhet District and Moulvibazar District in Bangladesh. They speak the endangered Laiunghtor ...
s, Bauris The Bauris (Bengali:বাউরী) are recognised as an indigenous Bhil Subgroup of Bengali Hindu community, belonging to the Kashyapa clan and Shakta sect of hinduism, primarily residing in Bengal found in large numbers in Bankura, Birbhum, Puru ...
and Tripuri
Tripuri refer to:
*Tripuri people, an ethnic group in India and Bangladesh, also known as Tipra people
**Tripuri language
**Tripuri nationalism
**Tripuri calendar
**Tripuri culture
**Tripuri cuisine
**Tripuri dances
**Tripuri dress
**Tripuri games ...
population. Sylhet has the largest concentration of Hindus in Eastern Bengal and is a part of the Shakti Peetha
The Shakti Pitha or the Shakti Peethas ( sa, शक्ति पीठ, , ''seat of Shakti'') are significant shrines and pilgrimage destinations in Shaktism, the goddess-centric denomination in Hinduism. The shrines are dedicated to various fo ...
.
Other minority religions include Christianity
Christianity is an Abrahamic monotheistic religion based on the life and teachings of Jesus of Nazareth. It is the world's largest and most widespread religion with roughly 2.38 billion followers representing one-third of the global pop ...
(including the Roman Catholic Diocese of Sylhet
The Roman Catholic Diocese of Sylhet ( la, Dioecesis Sylhetensis) is a diocese in Bangladesh, and comprises the civil districts of Sylhet, Sunamganj, Habiganj, and Moulvibazar. It lies in the Ecclesiastical province of Dhaka in Bangladesh.
Lea ...
and Sylhet Presbyterian Synod), Ka Niam Khasi, Sanamahism
()
, native_name_lang = mni
, image = The Symbol of Sanamahi.svg
, imagewidth =
, alt =
, caption = The Symbol of Sanamahism (Source: Wakoklon Heelel Thilen Salai Amailon Pukok Puya)
, ...
, Songsarek
The Garo is a Tibeto-Burman ethnic tribal group from the Indian subcontinent, living mostly in the Indian states of Meghalaya, Assam, Tripura, and Nagaland, and in neighbouring areas of Bangladesh, including Madhupur, Mymensingh, Haluaghat ...
as well as animism. In the early 20th century, there were over a hundred Marwaris from Rajasthan
Rajasthan (; lit. 'Land of Kings') is a state in northern India. It covers or 10.4 per cent of India's total geographical area. It is the largest Indian state by area and the seventh largest by population. It is on India's northwestern s ...
that were living in Sylhet, mostly as merchants and followed Jainism
Jainism ( ), also known as Jain Dharma, is an Indian religion. Jainism traces its spiritual ideas and history through the succession of twenty-four tirthankaras (supreme preachers of ''Dharma''), with the first in the current time cycle bein ...
.
There was a presence of Sikhism
Sikhism (), also known as Sikhi ( pa, ਸਿੱਖੀ ', , from pa, ਸਿੱਖ, lit=disciple', 'seeker', or 'learner, translit=Sikh, label=none),''Sikhism'' (commonly known as ''Sikhī'') originated from the word ''Sikh'', which comes fro ...
in Sylhet after Guru Nanak
Gurū Nānak (15 April 1469 – 22 September 1539; Gurmukhi: ਗੁਰੂ ਨਾਨਕ; pronunciation: , ), also referred to as ('father Nānak'), was the founder of Sikhism and is the first of the ten Sikh Gurus. His birth is celebrated w ...
's visit in 1508 to spread the religion. Kahn Singh Nabha
Kahn Singh Nabha (30 August 1861 – 24 November 1938) was a Punjabi Sikh scholar, writer, anthologist, lexicographer, and encyclopedist. His most influential work, Mahan Kosh, inspired generations of scholars after him. He also played a role in ...
has stated that in memory of Nanak's visit, ''Gurdwara Sahib Sylhet'' was established. This Gurdwara was visited twice by Tegh Bahadur
Tegh ( hy, Տեղ) is a village and the center of the Tegh Municipality of the Syunik Province in Armenia. Tegh is the last village on the Goris- Stepanakert Highway before passing the border with the Republic of Artsakh.
Of significance in the v ...
and many hukamnama
A Hukamnama (Punjabi: ਹੁਕਮਨਾਮਾ, translit. ''Hukamanāmā''), in modern-times, refers to a hymn from the Guru Granth Sahib which is given as an injunction, order, or edict to Sikhs. It also refers to edicts issued by the contempor ...
s were issued to this temple by Guru Gobind Singh. In 1897, the gurdwara fell down after the earthquake
An earthquake (also known as a quake, tremor or temblor) is the shaking of the surface of the Earth resulting from a sudden release of energy in the Earth's lithosphere that creates seismic waves. Earthquakes can range in intensity, fr ...
.
In popular culture
* In season 4, episode 6, of ''Call the Midwife
''Call the Midwife'' is a BBC period drama series about a group of nurse midwives working in the East End of London in the late 1950s and 1960s. The principal cast of the show has included Jessica Raine, Miranda Hart, Helen George, Bryony Ha ...
'', the midwives tend to a woman from the Sylhet Division.
See also
* Divisions of Bangladesh *List of people from Sylhet
This is a list of notable residents and people who have origins in the Sylhet Division of Bangladesh and the Barak Valley of the Indian state of Assam. This list also includes British Bangladeshis, Bangladeshi Americans, Bangladeshi Canadians, a ...
* Sylhet roofed turtle
* Sylhet Hara
References
External links
{{Authority control Divisions of Bangladesh